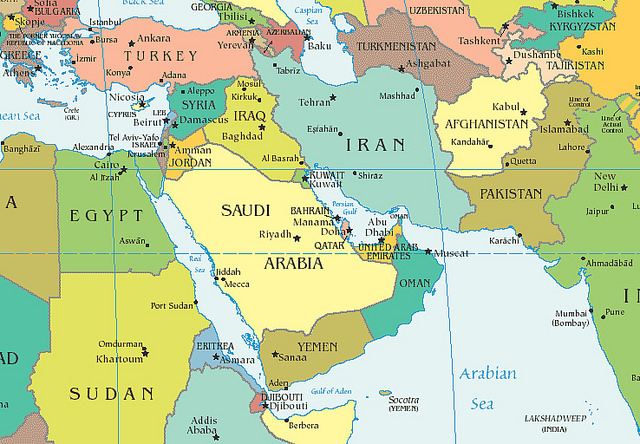
Early History. the center East has been called the cradle of civilization. quite 8,000 years ago, people during this part of the planet discovered the methods of agriculture that freed them from the necessity to wander about in search of food as hunters and gatherers. the event of settled communities and therefore the earliest sorts of government followed. Between 4000 and 3000 B.C., city-states, most notably Sumer, began to emerge within the southern part of the fertile region between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers.
Before the start of the Christian era, the center East had already seen the increase and eventual fall of various kingdoms and empires– those of the Egyptians, Hittites, Babylonians, Assyrians, and Persians among them. Their great contributions to civilization included codes of law, writing systems, mechanical inventions like the wheel, and therefore the development of sciences, like astronomy, and arithmetic. Judaism, the primary great monotheistic religion (the faith in but one God), evolved among a comparatively small group of individuals, the traditional Hebrews.
Click here to know about World History
Greeks, Romans, Arabs. Alexander the good invaded the region with a military of Macedonians and Greeks within the 300’s B.C. and carved out a huge empire supported Greek culture. The Romans began their own conquest of the region some three centuries later. When the Roman Empire within the West collapsed within the A.D. 400’s, its successor within the East, the Byzantine Empire, centered in Constantinople, endured for an additional thousand years. Meanwhile, the Arabs, newly converted to the Muslim religion by the prophet Mohammed, swept out of the Arabian Peninsula within the 600’s and created an Islamic empire.
The Ottoman Empire. Other conquerors– Seljuk Turks, European crusaders, and Mongols– followed in their turn. The last great empire of the region was that of the Ottoman Turks, who reached the peak of their power within the 1500s, when all of the center East, apart from Persia, came under their sway. From this part, Ottoman power slowly declined, although the crumbling empire was to last, a minimum of in name only, until the first 1900s.
Period of Nationalism. the ultimate breakup of what remained of the Ottoman Empire happened as a result of war I (1914-18), during which the Turks sided with the Central Powers, led by Germany and Austria-Hungary. Their defeat by the Allies, headed by Britain and France, split the empire apart, reducing Turkey to its present territory. During the war many Arabs rose in revolt against the Turks, fighting on the side of the Allies. The Arabs had hoped to realize their independence, but after the war, much of the region came under British and French control, as mandates of the League of countries (the forerunner of the United Nations).
Two Arab nations, Saudi Arabia and Iraq, came into being in 1932. Most of the remainder won their independence during or shortly after war II (1939-45). The last Arab countries to realize complete independence, the small Persian Gulf states, did so in 1971. The years after war II also marked the large-scale development of the region’s oil resources.
Recent History. within the years since the center, the East has frequently been torn by conflicts. Hostilities between the Arab countries and therefore the state of Israel, created by the United Nations in 1948 as a homeland for dispossessed Jews, has been the foremost long-lasting source of tension and has resulted in five wars between Israel and its Arab neighbors since 1949.
There are numerous other conflicts among countries of the region or within the borders of a rustic. Lebanon fought an extended war from the mid-1970s until 1990, and Iran and Iraq fought a bitter war from 1980 to 1988. Iraq invaded Kuwait in 1990 and refused to withdraw by the deadline set by the United Nations. within the Persian Gulf War that followed (1991), Iraq was quickly defeated by a U.S.-led international military coalition.
Israel had signed a peace with Egypt in 1979, but its relations with the remainder of the Arab world remained hostile until 1993. therein year, Israel and therefore the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) signed the primary during a series of accords granting limited self-rule to Palestinian Arabs and giving them authority within the Gaza Strip and the West Bank, areas occupied by Israel. Israel and Jordan also signed a peace, in 1994. Elections for a Palestinian self-rule authority were held in 1996, and Israel withdrew its forces from southern Lebanon in mid-2000.
For a time it seemed that the social process was irreversible. But the accords didn’t affect such controversial issues because of the future status of Jerusalem. A September 2000 deadline for reaching a final agreement wasn’t met, and a replacement cycle of violence began.